Explore the habitat, behavior, and control methods of pigeons in Arizona. Discover the different , their feeding habits, and the health concerns they pose. Stay informed about the regulations and responsibilities of property owners.
Habitat and Behavior of Pigeons in Arizona
Pigeons are one of the most common birds found in Arizona, particularly in urban areas. Their adaptability and resourcefulness have allowed them to thrive in various environments. Understanding their habitat and behavior can help us coexist with these avian neighbors.
Urban Pigeon Populations
Urban areas in Arizona provide an ideal habitat for pigeons. The availability of food, water, and shelter, combined with the absence of natural predators, has led to a significant increase in their populations. Pigeons are highly adaptable and can be found in cities, towns, and even suburban areas. Their ability to survive and reproduce in urban environments has made them a familiar sight to residents.
Migration Patterns
Unlike some bird species that migrate long distances, pigeons in Arizona are predominantly non-migratory. They have learned to take advantage of the year-round mild climate and abundant food sources. However, there may be some seasonal movements within the state in search of better foraging opportunities. These movements are usually short-distance and temporary.
Nesting Habits
Pigeons are known for their nest-building skills, and Arizona is no exception to this behavior. They prefer to build their nests in elevated areas, such as rooftops, ledges, and tree branches. Pigeon nests are typically constructed from twigs, leaves, and grass, providing a stable and secure structure for their eggs and young. The female pigeon lays one to two eggs at a time, and both parents take turns incubating them. Once the eggs hatch, the parents continue to care for the chicks until they are ready to leave the nest.
Pigeons have adapted well to urban environments, utilizing man-made structures for nesting. However, their nesting habits can sometimes lead to conflicts with humans, particularly when their nesting sites are on buildings or structures that can cause damage.
Pigeon Species Found in Arizona
Arizona is home to a diverse range of , each with its own unique characteristics and behaviors. Understanding these species is crucial for effective pigeon management and control. Let’s take a closer look at three common found in Arizona: Rock Pigeons, Eurasian Collared Doves, and White-winged Doves.
Rock Pigeons
Rock Pigeons, also known as city pigeons or street pigeons, are perhaps the most prevalent in Arizona. These adaptable birds are well-suited to urban environments and can be found in abundance in cities and towns across the state. Rock Pigeons have a distinctive appearance with their gray feathers, iridescent necks, and bright orange eyes.
These pigeons are highly social creatures, often seen in large flocks congregating on rooftops, ledges, and other structures. They have a remarkable ability to navigate their surroundings and find their way back to their roosting sites, even in unfamiliar territories. Their cooing calls are a familiar sound in urban areas, adding to the ambiance of city life.
Eurasian Collared Doves
Eurasian Collared Doves are another that has made its home in Arizona. Originally native to Europe and Asia, these doves were introduced to North America in the 1980s and quickly established thriving populations. They are slightly larger than Rock Pigeons and have a gray-brown plumage with a distinctive black crescent-shaped collar on the back of their necks.
Unlike Rock Pigeons, Eurasian Collared Doves are not as closely associated with urban areas. They can be found in a variety of habitats, including suburban neighborhoods, agricultural fields, and desert regions. These doves have a gentle cooing call that is often described as soothing and peaceful.
White-winged Doves
White-winged Doves are native to the southwestern United States, including Arizona. These large pigeons are known for their striking appearance, with white patches on their wings that are visible during flight. They have a gray-brown body and a distinctive blue eye ring.
These doves are commonly found in desert habitats, such as mesquite and saguaro forests. They are known for their distinctive cooing call, which is often described as a mournful sound. White-winged Doves are migratory birds, with populations in Arizona swelling during the summer months as they breed and raise their young.
(Word count: 414)
Pigeon Control Methods in Arizona
Pigeons can be a nuisance in Arizona, causing damage to structures and posing health risks. Fortunately, there are several effective methods available to control pigeon populations. In this section, we will explore three commonly used pigeon control methods: scare tactics, exclusion techniques, and repellents.
Scare Tactics
Scare tactics are a popular method for deterring pigeons from nesting or roosting in unwanted areas. These methods aim to create an environment that pigeons find intimidating or uncomfortable, encouraging them to seek alternative locations.
One effective scare tactic is the use of predator decoys. These life-like replicas of natural predators, such as owls or hawks, can be strategically placed in areas where pigeons tend to gather. The sight of these decoys can create a sense of danger for the pigeons, making them hesitant to settle in the area.
Another scare tactic is the use of visual deterrents, such as reflective surfaces or shiny objects. Pigeons are easily startled by sudden movements or bright lights, so hanging reflective tape or aluminum foil strips can help deter them. Additionally, devices that emit loud noises or ultrasonic sounds can also be effective in scaring pigeons away.
Exclusion Techniques
Exclusion techniques involve physically preventing pigeons from accessing certain areas. These methods aim to create barriers that deny pigeons entry or make it difficult for them to roost or nest.
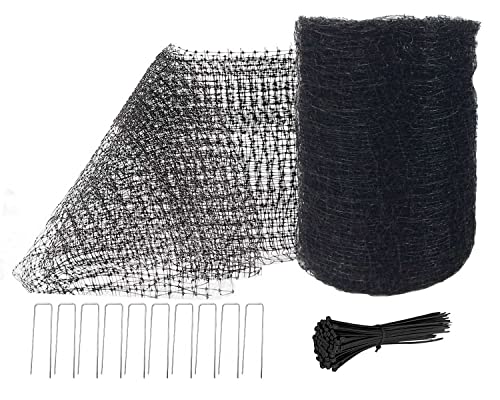
One commonly used exclusion technique is the installation of bird netting or mesh. These durable materials can be placed over openings or structures where pigeons are likely to gather. The netting acts as a physical barrier, preventing pigeons from entering and roosting in these areas.
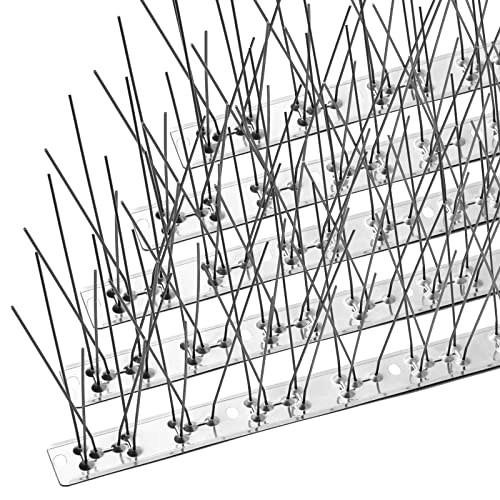
Another effective exclusion technique is the use of bird spikes. These are plastic or metal spikes that can be installed on ledges, beams, or other surfaces where pigeons tend to perch. The spikes make it uncomfortable for pigeons to land, discouraging them from settling in the area.
For areas with large open spaces, such as rooftops or courtyards, the installation of wire deterrents can be effective. These wires are strung across the area, creating an obstacle that pigeons cannot easily navigate or land on.
Repellents
Repellents are chemical substances designed to deter pigeons from certain areas. They work by emitting odors or tastes that are unpleasant to pigeons, making them avoid the treated areas.
One commonly used repellent is a bird gel or paste. This sticky substance is applied to surfaces where pigeons are likely to perch or roost. The gel creates an uncomfortable sensation on their feet, discouraging them from staying in the area.
Another type of repellent is an avian spray deterrent. These sprays contain natural or synthetic chemicals that emit odors or tastes that pigeons find repulsive. They can be applied to surfaces or vegetation to create an unpleasant environment for pigeons.
It’s worth noting that while repellents can be effective in certain situations, they may need to be reapplied periodically to maintain their effectiveness. Additionally, it’s important to choose repellents that are safe for both humans and the environment.
Remember, it’s important to consult local regulations and guidelines before implementing any pigeon control methods. Additionally, it may be helpful to seek professional assistance in determining the most appropriate and effective strategies for your specific situation.
Pigeon-Related Health Concerns in Arizona
Pigeons are a common sight in Arizona, often found in urban areas and known for their adaptability and resilience. While these birds may seem harmless, they can pose various health concerns for both humans and the environment. In this section, we will explore the spread of diseases associated with pigeons, the potential allergic reactions they can cause, and the damage they can inflict on structures.
Spread of Diseases
Pigeons can carry and spread several diseases, some of which can be transmitted to humans. One of the most well-known diseases associated with pigeons is histoplasmosis, a fungal infection caused by the inhalation of spores found in their droppings. When the droppings dry up and become airborne, the spores can be inhaled, leading to respiratory symptoms such as coughing, chest pain, and fever.
Another disease of concern is cryptococcosis, which is caused by a yeast-like fungus found in pigeon droppings. This infection primarily affects the lungs and can cause symptoms such as cough, shortness of breath, and chest discomfort. In rare cases, it can also spread to the central nervous system and cause meningitis.
Pigeons can also carry parasites such as ticks, fleas, and mites, which can transmit diseases to humans and other animals. These pests can cause skin irritation, allergic reactions, and in some cases, transmit serious illnesses.
Allergic Reactions
For individuals with allergies, pigeons can trigger allergic reactions. Pigeon feathers, droppings, and saliva can contain allergens that cause respiratory symptoms such as sneezing, coughing, and wheezing. These allergens can also lead to skin rashes and eye irritation.
In some cases, individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions such as asthma or chronic bronchitis may experience worsened symptoms when exposed to pigeon allergens. It is important for individuals with allergies or respiratory conditions to take precautions when in close proximity to pigeons or their nesting areas.
Damage to Structures
Pigeons can cause significant damage to structures, particularly when they roost or nest in buildings. Their droppings contain uric acid, which can corrode and decay surfaces over time. This can lead to structural damage to roofs, balconies, and other areas where pigeons congregate.
In addition to the corrosive nature of their droppings, pigeons can also cause blockages in gutters, drains, and ventilation systems. This can result in water damage, mold growth, and compromised air quality.
Furthermore, the accumulation of pigeon droppings and nesting materials can attract other pests such as rats and insects, creating additional problems for property owners.
To mitigate the damage caused by pigeons, it is important to address the issue proactively by implementing effective pigeon control methods and regularly maintaining affected structures.
Note:
The information provided above is for reference purposes only. It is important to consult with local authorities or professionals for specific guidelines and regulations related to pigeon-related health concerns and control methods in Arizona.
Pigeon Feeding Habits in Arizona
Food Sources
Pigeons in Arizona have a diverse range of food sources available to them, which contributes to their ability to thrive in urban and rural environments alike. These adaptable birds are known to consume a variety of foods, including grains, seeds, fruits, vegetables, and even small insects. In urban areas, pigeons often scavenge for discarded food from human activities, such as leftover crumbs from outdoor dining areas or improperly stored garbage. They are also attracted to bird feeders and can quickly consume large quantities of birdseed. In rural areas, pigeons rely more heavily on natural food sources, such as grass seeds and wild berries.
Feeding Behavior
Pigeons have a unique feeding behavior that allows them to efficiently gather and consume their food. They are ground-feeding birds, meaning they primarily forage on the ground rather than in trees or bushes. Pigeons use their beaks to pick up individual food items, and they have a specialized throat structure that enables them to swallow food whole. This efficient feeding behavior allows pigeons to quickly consume a large quantity of food in a short amount of time.
Pigeons are also known to exhibit flocking behavior while feeding. They often gather in large groups, especially in areas with abundant food sources. This behavior provides them with safety in numbers and allows them to collectively search for and identify food. Flocking behavior also enables pigeons to share information about food locations within the group, ensuring that all members have access to sufficient food resources.
Impact on Ecosystem
While pigeons may seem like harmless birds, their feeding habits can have significant impacts on the ecosystem. One of the main concerns is their ability to outcompete native bird species for food resources. Pigeons’ adaptability and large population sizes can result in the depletion of food sources for other bird species, potentially leading to decreased biodiversity in certain areas.
Additionally, pigeon droppings can have negative effects on the environment. Pigeon populations produce a large volume of feces, which can accumulate in urban areas and pose risks to human health. The droppings contain high levels of nitrogen, which can contribute to water pollution if they wash into rivers, streams, or other water bodies. The accumulation of pigeon droppings can also damage vegetation and buildings, as the high nitrogen content can act as a fertilizer, promoting excessive growth of certain plant species and causing structural corrosion.
- Food sources for pigeons in Arizona include grains, seeds, fruits, vegetables, and small insects.
- Pigeons primarily forage on the ground and have a specialized throat structure for swallowing food whole.
- Flocking behavior allows pigeons to share information about food locations and ensures access to sufficient resources.
- Pigeon feeding habits can lead to competition with native bird species and contribute to environmental pollution.
Pigeon Management Regulations in Arizona
Arizona has implemented various pigeon management regulations to address the population control and potential issues associated with pigeons. These regulations aim to strike a balance between protecting public health and ensuring the well-being of property owners. Let’s explore the specific aspects of pigeon management regulations in Arizona.
Local Pigeon Control Laws
Local governments in Arizona have enacted specific pigeon control laws to address the challenges posed by these birds. These laws typically outline guidelines for managing pigeon populations within city limits. They may include provisions related to feeding restrictions, roosting prevention, and the use of certain control methods.
One of the most common pigeon control laws is the prohibition of feeding pigeons in public areas. Feeding pigeons can contribute to population growth and create health hazards. By discouraging pigeon feeding, local authorities aim to reduce the availability of food sources and discourage pigeons from congregating in specific areas.
Additionally, local pigeon control laws may address issues such as the installation of bird deterrents on buildings or the use of noise devices to discourage roosting. These measures help prevent pigeons from nesting and roosting on structures, reducing potential damage and health risks.
Permits and Licenses
In some cases, property owners or pigeon control professionals may be required to obtain permits or licenses to implement certain pigeon control methods. These permits ensure that control measures are conducted safely and responsibly.
For example, if a property owner wishes to use trapping or culling methods to reduce pigeon populations, they may need to obtain a permit from the appropriate local authority. This permit ensures that the methods used are humane and comply with regulations.
Similarly, professional pigeon control companies may need to obtain licenses to offer their services in Arizona. These licenses often require the company to demonstrate their expertise in pigeon management and adhere to specific guidelines for control methods.
Responsibilities of Property Owners
Property owners in Arizona have certain responsibilities when it comes to managing pigeons on their premises. These responsibilities are designed to minimize the impact of pigeons on public health and property.
One such responsibility is the maintenance of pigeon-proofing measures on buildings. Property owners are encouraged to install deterrents such as netting, spikes, or wire barriers to prevent pigeons from roosting or nesting on their structures. Regular inspections and repairs of these deterrents are also recommended to ensure their effectiveness.
Property owners should also promptly address any pigeon-related issues on their properties. This includes cleaning up pigeon droppings, removing nests, and repairing any damage caused by pigeons. By taking proactive measures, property owners can help prevent the spread of diseases carried by pigeons and maintain the integrity of their structures.
In conclusion, Arizona has implemented pigeon management regulations to address the challenges posed by pigeons. These regulations include local pigeon control laws, permits and licenses for certain control methods, and responsibilities for property owners. By adhering to these regulations, Arizona aims to ensure public health and minimize the impact of pigeons on properties.